We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
Blog - How do I calculate a spring rate of an torsion spring?
The function of a Torsion Spring is to withstand a certain radial pressure or angular deflection. A torsion spring is produced with so-called legs and coils. The leg length largely determines the strength and force to be transmitted. The turns determine the force of the spring and the number of degrees of rotation that are possible. The shape of the spring is largely determined by the available space, the material to be used and the spring constant. The single wound torsion springs are available Left and Right wound version. More general information about torsion springs.

This piece explains:
- What is a spring constant per ° twist.
- The formula of spring rate for torsion springs.
- Application of a spring rate of torsion springs.
- Which parameters influence the spring constant of torsion springs.

What is a spring constant per ° of twists?
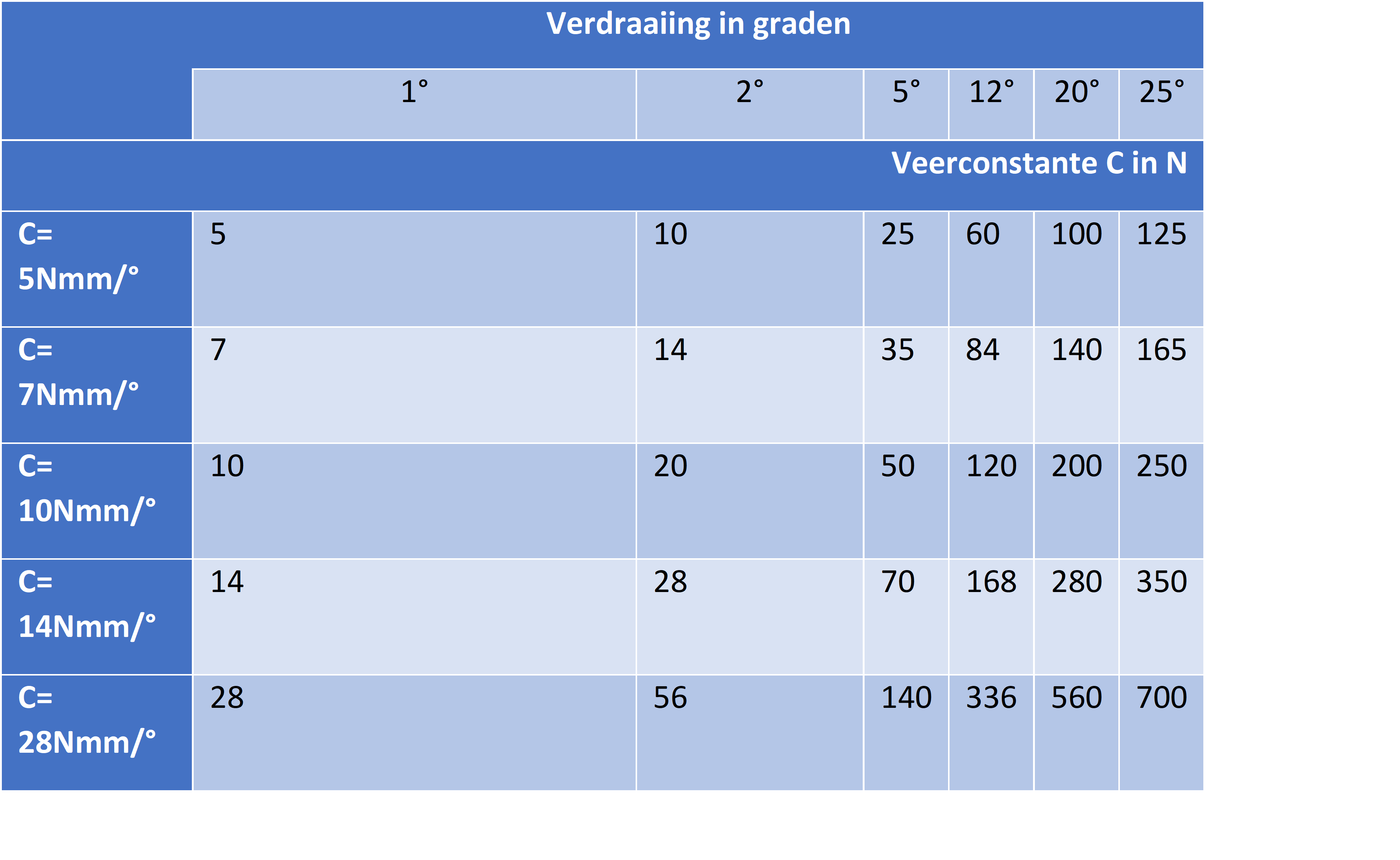
The spring constant of a torsion spring is a linear relationship, the spring travel and force are even related to each other. A spring constant for a torsion spring differs from a compression spring constant. The spring constant of this spring is indicated as Nmm/°. The spring constant is a unit that can be used to determine how much force a spring produces at a certain angular displacement. So suppose a spring has a spring constant of 5Nmm/° this means that with every extra degree of rotation the spring delivers a force of which every extra degree becomes 5N stronger.
For example:
Torsion spring rate formula
To calculate the spring constant of a torsion spring, a number of parameters are needed. The wire thickness, the diameter center to center and the number of turns. The modulus of elasticity depends on the material. Request the specifications of the elastic modulus of a certain steel in wire thickness from your spring supplier, or send an email to one of our sales departments.
C = Spring constant in N/mm°
E = Elasticity modulus (In MPa)
d = Wire thickness in mm
Dm = Diameter Center to Center in mm
Nw= Number of turns/coils
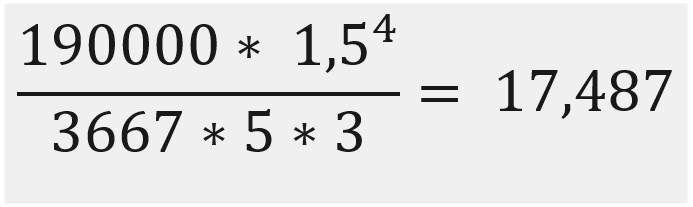
As an example the following calculation. The 17.487 is then the N/° of spring constant that is in the torsion spring.
How do you apply a spring rate to Torsion Springs?
The spring constant is a calculation that shows the strength of the windings. The spring constant is, so to speak, the force in the spring. A Moment is used to calculate the forces of torsion springs. There is an difference between a Moment and the spring constant. The object to be pushed of a torsion spring is placed on the legs, the legs have a force-transferring function. The function of legs on torsion springs, is to transmit force, is a secondary lever effect. In order to properly apply the obtained spring constant, we have to include the legs. We call this a Moment. Torsion springs have a wide tolerance with regard to the force, we do not take the tolerances in account with this calculation. We recommend to ask for a drawing of the torsion spring and an implantation of the goodman diagram for all torsion springs.
For example torsion spring TS100330R:
Spring constant = 0.06 Nmm/°
Leg length= 16 mm
One moment ( M ) is always standardly measured on the half of the leg length (a) in this example the leg length is 16 mm so we calculate it at 8 mm.
M=F * a
M=0.06 * 8
M = 0.48 Nmm/°
Subsequently, the torsion force from the lever can be calculated with this. Example if we want to move an object of 1 kg with the torsion spring TS100330, 9.810 Newton is needed.
Here the calculation is ° = Object N / M.
9.810 / 0.48 = 20.4375°.
To move this object, the torsion spring leg must turn 20.4375 degrees.
How do I change the Nmm/° on a torsion spring?
There are three dimensions that have a strong influence on the torsion spring. With these three parameters, springs can be developed to deliver more or less force. Always have a Goodman Chart made for the desired application. This determines at the spring whether the application is realistic. The three parameters that strongly determine the Nmm/° of a torsion spring are:
- Wire diameter
- Spring diameter
- Number of active turns
There is always the choice to take more or less. If more effective turns are placed on the torsion spring, the spring becomes weaker. Fewer active turns make the spring stronger. Taking a larger wire diameter of a spring makes the spring stronger and the opposite, a smaller wire diameter makes the spring weaker. A larger diameter of a spring (Dm center to center) makes the spring weaker, while a smaller diameter makes the spring stronger.
Order torsion springs
Have your torsion springs made by a spring specialist. All torsion springs are standard available in spring steel or stainless steel 301 via the webshop. Position of the legs according to drawing, stating A/B/C/D position (articles beginning with TS). Additional bends can be added to the arm in consultation. We can also produce torsion springs according to customer specifications. Besides the ordinary spring steel and stainless steel 302, we make springs of inconel, titanium, ninomic, phosphor bronze, tungsten and the like. Our engineering department can help you choose the right material for your application and assist you in finding and calculating the right spring. In addition, we can provide various after-treatments such as chrome plating, nickel plating, chemical blackening, epoxy coating, tin plating, galvanizing, pickling and passivation, electrolytic polishing, gold plating, silver plating, cleanroom packaging and the like.